BLOG
Considerations for Investing in DSTs and Debt Replacement Requirements

Revenue Ruling 2004-86 addresses the qualification of DSTs as potential Replacement Property in a 1031 Exchange under Internal Revenue Code (IRC) Section 1031. In this ruling, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) acknowledges that an exchange of real property for a beneficial interest in a Delaware Statutory Trust (DST), which owns real property, is considered a like-kind exchange under Section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code. This was a groundbreaking Revenue Ruling because it imposed stricter standards of the ownership structure and use of property held in a DST than was previously found in Revenue Procedure 2002-22, which currently regulates the Tenants in Common (TIC) form of ownership.
The ruling considers the nature of a DST, which are recognized as separate entities from their owners under Delaware law, with beneficial interests considered personal property. However, for federal income tax purposes, these beneficial interests are treated as direct ownership of the underlying real property assets, allowing for the tax-free exchange under Section 1031. This means that a 1031 Exchange can be carried out without immediate tax consequences, as the beneficial interest in the DST is treated as equivalent to direct ownership of real property for the purposes of the exchange.
Overview of Delaware Statutory Trusts (DSTs)
Accredited Investor Standard
To qualify for investment in a DST, an Exchanger must be an Accredited Investor. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) provides guidelines for who may qualify as an Accredited Investor, which includes measures of wealth, income, and financial sophistication. To qualify as an Accredited Investor based on net worth, an individual must have a net worth over $1 million, excluding the value of the primary residence, either individually or jointly with a spouse or partner. For income-based qualification, an individual must have had an income over $200,000, or a combined income of $300,000 with a spouse or partner, in each of the prior two years and expect the same for the current year.
In the realm of private placements, the verification of an Exchanger’s Accredited Investor status is a critical step that sponsors of DSTs must undertake. This process is not only a regulatory requirement, but also a measure to protect both the sponsor and the investor. Typically, the verification involves a thorough review of financial documentation provided by the Exchanger, which may include a detailed financial questionnaire. The questionnaire often covers aspects such as income, net worth, investment experience, and risk tolerance. Additionally, the sponsor may request financial statements or other supporting documents to substantiate the information provided in the questionnaire.
This due diligence ensures that the investor meets the specific criteria set forth by the SEC for Accredited Investors, which, in turn, qualifies them to partake in DST investments. It's a safeguarding protocol that maintains the integrity of the investment process and upholds the standards of the private securities market.
DST Structure
A DST is a legal entity under Delaware law that allows up to 2000 investors. Investors have no management rights or voting power, only quarterly income distribution rights proportional to their respective beneficial interests. A DST Sponsor establishes the DST for holding real estate assets, acquires properties to include within the DST’s portfolio, and develops the investment offering detailing the potential returns and risks for investors. Sponsors also dictate when to sell properties within the Trust, ensures compliance with all regulatory requirements and filings associated with the DST, and communicates with investors regarding the performance and management of the real estate assets. The DST's management is handled by a signatory trustee, not the Delaware trustee, whose role is limited.
Lenders favor DSTs over TIC because they involve a single loan to one entity rather than multiple owners, reducing complexity and bankruptcy risks. For federal tax purposes, a DST is treated as a Trust if it adheres to certain "fixed investment trust" criteria; otherwise, it may be considered a partnership or corporation.
The DST must not be traded on an established securities market, and its trustee is limited to specific administrative duties, primarily the collection and distribution of income to the beneficial owners. The beneficial interests in the DST are treated as interests in a grantor trust, with the owners deemed to hold undivided fractional interests in the DST's real property for federal tax purposes.
DST Restrictions Under Revenue Ruling 2004-86
The Revenue Ruling imposes significant restrictions on the powers of the DST's trustee, colloquially referred to as the "seven deadly sins," to ensure that the DST does not operate as a business entity, which would disqualify it from 1031 exchange eligibility. These prohibitions include the trustee's inability to:
- Dispose of the Trust's assets and acquire new ones, except for the dissolution of the trust following a sale.
- Purchase assets other than short-term investments.
- Accept additional contributions to the Trust after the initial offering is closed.
- Renegotiate or refinance the debt on the property, unless necessitated by a tenant's bankruptcy or insolvency.
- Renegotiate leases or enter into new leases, except in cases of tenant bankruptcy or insolvency.
- Retain cash other than necessary reserves, instead of distributing it to beneficiaries.
- Make substantial modifications to the property, barring legal requirements.
These limitations are designed to prevent the DST from being classified as a partnership or corporation for federal tax purposes, which would invalidate the beneficial interests as Replacement Property in a 1031 Exchange. Due to these constraints, DSTs are typically most appropriate for properties with long-term, triple-net leases to creditworthy tenants as the graphic below illustrates. This structure allows for passive, in lieu of active investment, aligning with the intent of IRC Section 1031 to defer capital gains taxes through like-kind exchanges.
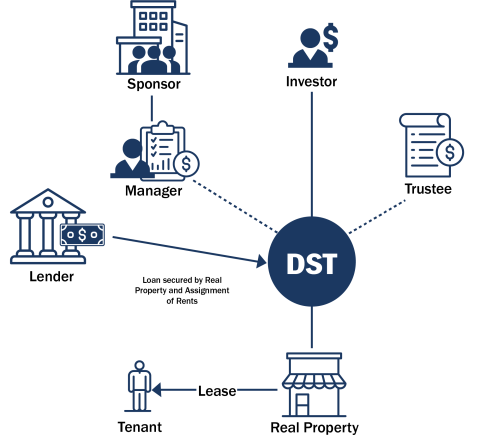
Entry Points in a DST
When an Exchanger is considering a DST as Replacement Property there are two common entry points to start the process, each being regulated differently, as discussed below.
Registered Investment Adviser (RIA)
Many Accredited Investors will have an RIA and therefore they are a common channel for entering the DST market. Under the fiduciary standard, an RIA must prioritize their clients' interests above their own, ensuring that advice given is in the client's best interest. This includes a commitment to transparency, honesty, and diligence, avoiding conflicts of interest, and making decisions that align with the client's financial goals and risk tolerance. Fiduciaries have a duty to evaluate the full spectrum of a broker-dealer's services, not just the commission costs, and ensuring clients are not burdened with unnecessary expenses. Regular assessment of the broker-dealers' performance is crucial to uphold the best execution standard. Additionally, fiduciaries must disclose any potential conflicts of interest and obtain informed consent from clients before proceeding with transactions that may affect them. RIAs are regulated by the SEC and when engaging in placing a client in a DST usually obtain a due diligence fee but cannot charge a commission. RIA’s earn fees to manage assets and grow wealth, versus a transactional-based sale of a security in the case of a broker/dealer as discussed below who are commission based.
Broker Dealers
Brokers of DST beneficial interests are often regulated under the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA). Brokers typically earn up to a 7% commission on the sale of a beneficial interest in a DST. Under FINRA, Brokers are bound not by a fiduciary standard, but rather a suitability standard. FINRA Rule 2111 is designed to ensure that investment recommendations made by broker-dealers or associated persons are suitable for their customers. The rule mandates that these professionals must perform due diligence to understand a customer's investment profile, which encompasses a range of factors from age and financial situation to investment goals and risk tolerance.
Debt Replacement and Exchange Value
As with any 1031 Exchange, the equal or up in value rule requires Exchangers to roll over all the net equity from the sale and have equal or greater debt on the new property. If an Exchanger fails to reinvest all the cash generated from the sale of Relinquished Property, they will incur a taxable event referred to as “cash boot.” If an Exchanger fails to take on debt on Replacement Property equal or greater to the debt payoff on the Relinquished Property, they will incur a taxable event referred to as “mortgage boot.” If Exchangers satisfy the equal or up in value rule, they will generally not incur a taxable event in the 1031 Exchange from mortgage boot or cash boot received.
Familiarity with this concept matters because in a leveraged DST, Exchangers acquire a beneficial interest in a trust that holds debt-financed properties. A lender for the property makes one loan to the DST. The leverage ratio, which is the amount of debt compared to equity, can vary. For instance, a 50% leverage means that half of the Trust's portfolio value is financed through debt. Under Delaware law, beneficial owners are not liable for the obligations of the DST. However, even though the debt is non-recourse to the Exchanger, they receive credit towards the debt replacement requirement under Sec. 1031 when selling property leveraged with recourse debt as discussed below.
For Exchangers to eliminate the possibility of mortgage boot, a taxable event, the DST must have a similar debt-to-equity ratio when compared to the Relinquished Property the Exchanger sold to comply with the equal or up in value concept.
Historically, Relinquished Property sales average about 25% loan to value (LTV). So, when it pertains to DST LTV, the exchange party needs to pay close attention to acquiring equal or greater non-recourse debt to prevent a taxable event.
If the ratios are not aligned between the Relinquished Property LTV and newly acquired DST LTV, adjustments can be made to match the required debt replacement. For example, if the Exchanger is selling at 25% LTV and acquiring at 55% LTV in a leveraged DST, then there is no equal or up violation so long as all equity is reinvested because the Exchanger acquired more debt than they relinquished. However, if selling at 60% LTV and acquiring at 55% LTV in a leveraged DST, then mortgage boot would occur as to the 5% variance, unless the exchange party offsets fractionally with another leveraged DST portfolio to average out at 60% LTV or injects 5% fresh equity, cash, into the purchase to offset the LTV variance.
Passive Investment Debt Replacement Calculator
Reinvesting all debt and equity generated from the sale of Relinquished Property is more nuanced when acquiring a DST, because each single asset DST or portfolio DST will have a unique LTV. Additionally, the Exchanger has no control over the LTV on a particular DST, they merely have to decide which, if any, of the investments are a fit for them.
To simplify the process of ensuring debt is replaced equal or up in value in a passive real estate investment, Accruit created a Debt Replacement Calculator. First, accurately input the Relinquished Property details including the debt payoff on the Relinquished Property. Next, an Exchanger can input one or more unique DST Replacement Properties and their associated LTV to assess the potential for a taxable event based on mortgage or cash boot.
It's important for Exchangers to consult with tax professionals to understand the specific implications of this calculator on an individual situation. Although DST debt is non-recourse, if an Exchanger exits a DST interest upon the Sponsor selling the asset and then decides to acquire a fee simple interest, such as a single-family rental home, as Replacement Property, they will need to replace the non-recourse debt with recourse debt or inject fresh equity (i.e. cash infusion) to prevent mortgage boot. This is particularly important to flag as oftentimes investors are encouraged to “double up” on non-recourse debt with passive real estate investments, which will obviously cause exit issues with mortgage boot as discussed above.
Additional DST Considerations
DST as Pure Debt Replacement Option
A “zero-coupon” leveraged DST portfolio is an investment structure where the Trust does not pay out earnings but instead reinvests them, allowing the value of the investment to grow over time. This type of portfolio is often leveraged significantly, sometimes at 80% or higher, which means that for every dollar of equity, there are four dollars of debt. While this can amplify gains if the property appreciates, it also increases risk. The zero-coupon aspect means that investors do not receive regular income distributions, but they may benefit from the potential appreciation of the property's value over time.
If you are selling an investment property for $1,000,000 but there is a loan outstanding for $800,000, then you at 80% LTV. Exchangers may creatively employ the use of a zero-coupon DST to prevent incurring mortgage boot by acquiring a beneficial interest in a zero-coupon DST as to their remaining debt to satisfy the debt replacement requirements under the equal or up in value rule. For instance, if the Relinquished Property was over leveraged, the acquisition of a zero-coupon DST matching the LTV of the Relinquished Property would allow the Exchanger to reinvest their recourse debt into non-recourse debt in the Replacement Property DST and not incur a taxable event related to that debt payoff. <
Umbrella Partnership Real Estate Investment Trust (UPREIT)

Section 1031 does not allow a direct exchange into a partnership or LLC interest since those interests are not classified as real property interests. An example is an investment in a Real Estate Investment Trust (“REIT”). The interests are just paper membership certificates that gives an investor an interest in the partnership and not the real property owned by the partnership or LLC. Even though the REIT is a denominated as a “trust” it is actually taxed as a partnership, usually has multiple co-owners, and sometimes is large enough to be publicly traded on the stock exchange.
An UPREIT offers a unique investment structure that allows for the deferral of capital gains taxes through a combination of 1031 Exchange and 721 Exchange. Exchangers without institutional-quality real estate can combine 1031 and 721 to ultimately invest into a REIT. Neither step triggers capital gains taxes. First, the 1031 Exchange facilitate by the Qualified Intermediary permits Exchangers to swap real estate for a beneficial interest in a DST which holds institutional-grade property. This step is tax-deferred, maintaining the investor's capital gains tax liability.
Next, the 721 Exchange, coordinated by the DST Sponsor, which occurs a couple years later, allows the contribution of the DST interest to a REIT operating partnership in exchange for Operating Partnership units (“OP units”), again deferring capital gains taxes. Functionally, the 721 Exchange allows a REIT to purchase a property from a DST at its fair market value. In return, the investor holding a beneficial interest in the DST is compensated with OP units in the REIT. This transaction is governed by Section 721 of the Internal Revenue Code. It's a sophisticated process that offers Exchangers the opportunity to transition from direct property ownership to holding a share in a diversified real estate portfolio managed by the REIT, while deferring capital gains taxes when properly executed. The OP units received are typically valued equivalently to the contributed property and carry similar tax benefits to direct real estate ownership, such as depreciation. However, it's important to note that converting OP units into common shares of the REIT might trigger a taxable event.
This two-step 1031/721 process provides exchangers with several benefits. Firstly, it enables access to a diversified portfolio of high-quality real estate managed by professionals, which might be beyond the reach of individual exchangers otherwise. Secondly, it offers the possibility of permanent tax deferral, as heirs can receive a stepped-up basis in the OP units upon the investor's death, potentially erasing the deferred tax debt. Additionally, the full divisibility of OP units allows for greater flexibility in investment decisions, and the active management of the portfolio can lead to enhanced performance over time. It's important to note that to participate in a 721 Exchange, the property contributed must typically be of institutional-grade quality, which may not be a feasible option for all Exchangers. However, by first converting a nonqualifying property into a DST interest through a 1031 exchange, exchangers can effectively upgrade their holdings to meet the criteria for a 721 Contribution with a REIT. This strategic maneuvering within the real estate market can be an effective way for exchangers to defer capital gains taxes while gaining exposure to premium real estate assets.
In conclusion, DSTs, and other forms of passive real estate investments are becoming increasingly popular for investors. Our goal is to unpack the overall process, structure, and general requirements to achieve tax deferral through a 1031 Exchange for any of these investments. As always, Exchangers should consult with their tax preparer to understand the implications fully and ensure compliance with all tax laws and regulations including the necessary holding period required prior to investing into any of these avenues.
The material in this blog is presented for informational purposes only. The information presented is not investment, legal, tax or compliance advice. Accruit performs the duties of a Qualified Intermediary, and as such does not offer or sell investments or provide investment, legal, or tax advice.

